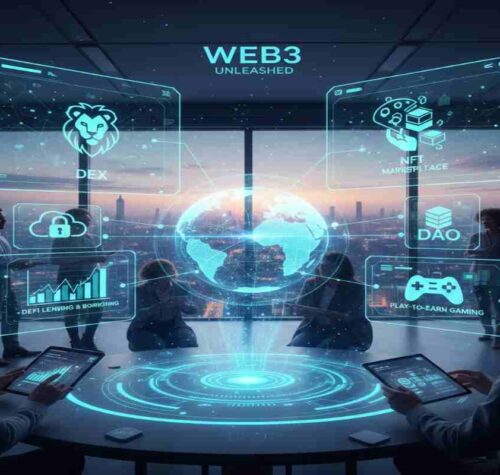
Web3 Applications Explained: Use Cases That Actually Work
Web3 applications create real value only in narrow, trust-minimized use cases like finance and digital ownership—not as a universal replacement for Web2 apps.
That single sentence answers the main question most people searching.